Research Overview
Overview of the Research
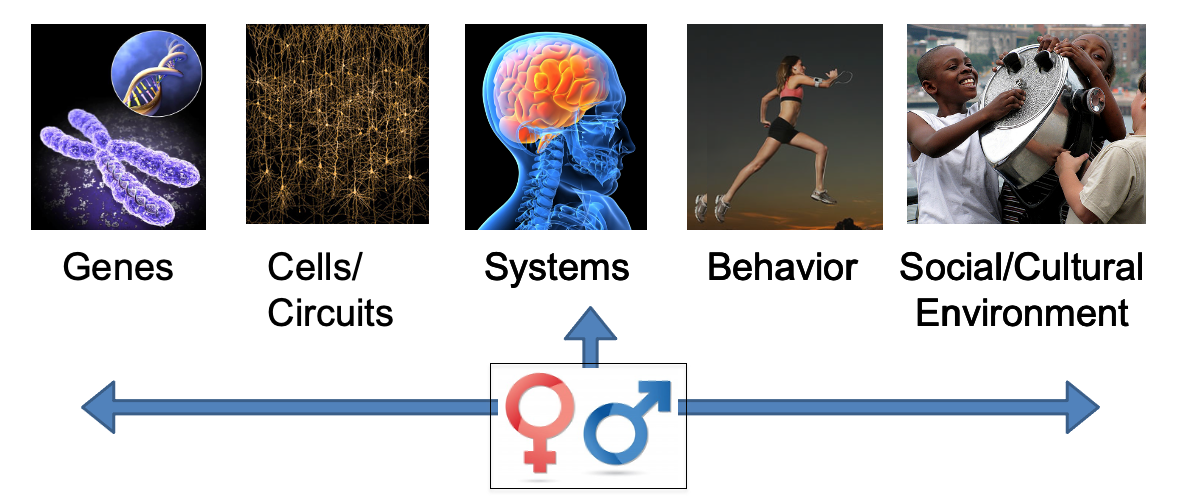
The CNL-SD focuses on understanding why there are substantial sex differences in disorders of the brain and how to use this knowledge to develop more efficacious therapies. We take a lifespan approach to thinking about risks and resilience beginning in fetal development. We are particularly interested in shared pathophysiology for understanding sex differences in the brain and comorbid cardiometabolic disorders. The team consists of interdisciplinary investigators integrating structural and functional imaging (i.e., sMRI/fMRI/DTI), psychophysiology (e.g., heart rate/autonomic nervous system), hormones, genes, metabolism, and immune biomarkers. We collaborate with basic neuroscientists investigating steroid hormones, genes, immune pathways, and the brain.
Functional domains of interest include the stress response circuitry (mood and anxiety), memory circuitry (long- and short-term memory), and emotion regulation changes with age. Current NIH-funded projects investigate these brain circuitries in depression and its comorbidity with cardiometabolic disorders. Included in this work, Goldstein and colleagues have been following a prenatal cohort over the last 30 years (initiated in 1959-1966 following pregnant mothers and their offspring for 7 years), allowing us to re-recruit offspring as 50–60-year-old adults and study in vivo the fetal programming of sex differences in adult-onset diseases. This work contributes to understanding the nature of disorders of the brain, the impact of sex and its impact on the course of healthy development and disease.
Our current topics
-
Sex impacts the brain beginning in fetal development, differences that are retained across the lifespan.
-
Depression & CVD are the primary causes of disability worldwide, and women are at twice the risk than men.
-
Development of novel devices targeted to the neural-cardiac interface will contribute to attenuating comorbidity of depression & CVD.
-
Women and men have different risks and resilience for disorders of aging; understanding these differences is critical to maintaining brain health into old age.
-
The impact of sex on risk, course, prognosis, and treatment response in schizophrenia is critical to understand in order to target early for prevention.
-
Our lab draws on three sources of participants:
The New England Family Study (NEFS)
The MGB Biobank
The general population (community participants)